
Cardiovascular fitness is not only an essential part of your workout routine but also fundamental to overall health, affecting your endurance, energy levels, and even longevity.
Many people know that exercise is essential for a healthy lifestyle, but why is cardiovascular fitness so important?
Incorporating cardiovascular workouts into your routine is crucial for overall health, benefiting everything from your heart and lungs to your mental well—being.

Cardiovascular fitness, often referred to as aerobic exercise, improves your body’s ability to deliver oxygen—rich blood to muscles and helps them use this oxygen efficiently for sustained physical activity. Cardio involves activities that:
Improve the heart and lungs’ ability to supply oxygen—rich blood to working muscles.
Enhance the muscles’ capacity to use oxygen efficiently, supplying energy for movement and endurance.

Aerobic exercise enhances cardiovascular fitness and encompasses any rhythmic, continuous activity that involves multiple large muscle groups.
These types of cardiovascular activities place a beneficial challenge on the heart and lungs, prompting them to work harder and become more efficient over time.
To maximize benefits from cardiovascular exercise, it’s crucial to maintain your heart rate within a target heart rate zone.
This is typically calculated by subtracting your age from 220 and then identifying 60–85% of that number as your target range.
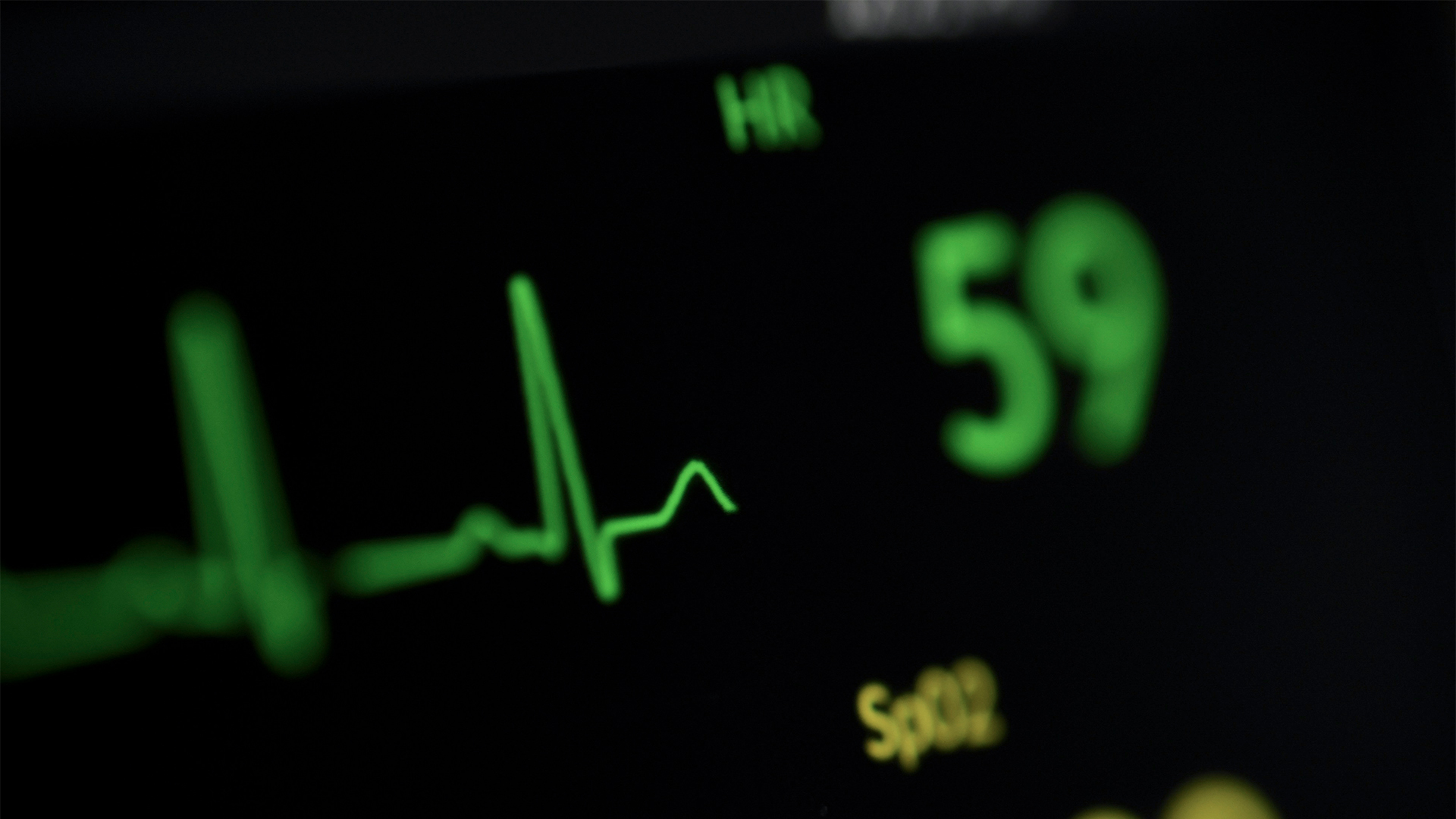
Example: If you are 30 years old:
Subtract your age from 220 to find your maximum heart rate:
220 – 30 = 190 beats per minute (bpm)
Calculate 60–85% of your maximum heart rate to determine your target heart rate range:
60% of 190 = 114 bpm
85% of 190 = 162 bpm
So, for a 30—year—old, the target heart rate range during cardiovascular exercise would be approximately 114—162 bpm.
This range helps ensure you’re working at an intensity that maximizes cardiovascular benefits while staying safe.
Achieving and maintaining optimal cardiovascular health doesn’t happen by chance. It requires a consistent, balanced approach to exercise and heart—healthy habits. Common examples include:
Running or Jogging: A classic choice that improves cardiovascular endurance.
Cycling: A joint—friendly option that builds leg strength while boosting heart health.
Power Walking: A low—impact activity that can be as effective as jogging.
Stair Climbing: Whether on a machine or on real stairs, it challenges the heart and leg muscles.
Aerobics Classes: These offer varied routines that engage different muscle groups.
Interval Training: Short, intense bursts followed by rest periods that maximize calorie burn.
Certain Yoga Practices: Dynamic forms like Vinyasa can also boost cardiovascular health.
Incorporating various aerobic exercises such as running, cycling, and interval training ensures that your cardiovascular system stays strong and effective.
Cardiovascular fitness is integral to heart health. Regular aerobic exercise strengthens the heart muscle, making it more efficient at pumping blood.
In simple terms, the easier it is to pump blood through your body, the less taxing it is on your heart. This, in turn, helps:
Lower blood pressure.
Improve circulation and the health of blood vessels.
Decrease harmful cholesterol levels (LDL) while boosting good cholesterol (HDL).

One of the most effective ways to manage or lose weight is through regular cardio workouts. Here’s how:
Calorie and Fat Burn: Both high—intensity and low—intensity cardio can help burn calories, though HIIT (High—Intensity Interval Training) tends to burn more total calories over shorter periods.
Boosts Metabolism: Regular cardiovascular training enhances the body’s ability to burn calories at rest by improving metabolic rate.
Fat Utilization: During aerobic exercise, the body utilizes stored fat for energy, which helps in reducing body fat over time. The fat you store on your body is reserved for periods of prolonged or intense activity. Training the cardiovascular system through high intensity intervals increases the activity of certain hormones, such as testosterone and growth hormone, that enhance fat burning.
The efficiency of oxygen usage is a crucial benefit of cardiovascular fitness. As your fitness level improves, for example, after an extended period of performing regular aerobic exercise, your body makes numerous adaptations that result in improved cardiovascular fitness. The muscles involved in respiration (intercostals and diaphragm):
Get stronger and more efficient
Increase capillary density, allowing better oxygen delivery.
Boost mitochondrial function, improving energy production.
Engaging in regular cardio workouts leads to significant long—term adaptations in heart health. One major benefit is the increase in stroke volume, which is the amount of blood the heart pumps with each beat.
This adaptation results in a lower resting heart rate, indicating that your heart has become more efficient and doesn’t need to work as hard during rest.
Additionally, enhanced cardiac output means more blood is pumped with each beat, improving oxygen distribution throughout the body and supporting overall cardiovascular efficiency.
Consistent aerobic exercise can also boost lung capacity, allowing you to take in more oxygen with each breath.
This not only enhances your exercise performance but also improves your daily energy levels.
Cardiovascular fitness strengthens the respiratory muscles, such as the diaphragm, leading to deeper, more controlled breathing.
Over time, this adaptation promotes more efficient oxygen exchange, which is essential for maintaining stamina and reducing fatigue during physical activities.
Start by choosing activities you enjoy to ensure long—term adherence. The key to sustaining a cardiovascular fitness routine is to choose activities you genuinely enjoy. Whether it’s playing sports, cycling, or dancing, selecting a form of exercise you look forward to can ensure long-term adherence. Here are some tips:
Start Slow: If you’re new to cardio, begin with lower—intensity activities like walking or cycling. Gradually build up your stamina and intensity over time to prevent injuries and allow your body to adapt.
Mix It Up: Incorporating variety into your workouts can prevent plateaus and keep things engaging. Alternating between steady-state cardio and High—Intensity Interval training (HIIT) sessions can maximize your fitness gains and promote cardiovascular health. Sports like football (soccer), basketball, or tennis offer fun, dynamic cardio workouts that engage multiple muscle groups and maintain motivation.
Monitor Progress: To track your progress and ensure you’re working effectively, monitor your heart rate during exercise. Most fitness experts recommend working within 60—85% of your maximum heart rate (calculated as 220 minus your age) for optimal aerobic benefits.
Stay Consistent: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate—intensity or 75 minutes of high—intensity aerobic exercise per week, as per health guidelines.
Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is crucial for supporting endurance and aiding recovery after workouts.
Pair with Strength Training: This combination maximizes overall fitness and boosts your metabolic rate, allowing you to build muscle and burn calories more efficiently.

Regular participation in cardio exercises, such as jogging, cycling, or playing sports, releases endorphins—your body’s natural mood elevators.
This release helps reduce anxiety levels and enhances mood, making it easier to manage daily stressors. Whether it’s a solo run or a recreational game of basketball, cardio activities can provide a mental break and improve your emotional state.
Cardio isn’t just beneficial for your body—it also improves your brain health.
Engaging in regular aerobic exercise increases blood flow to the brain, which can enhance memory and cognitive function.
Over time, maintaining consistent cardiovascular fitness can lower the risk of cognitive decline as you age and support long—term brain health.
Supports Longevity
Studies have shown that regular cardiovascular exercise can contribute to a longer life. By improving heart health, managing weight, and enhancing overall body function, cardio plays a significant role in promoting longevity.
Enhances Sleep Quality
Regular aerobic activity can help you fall asleep faster and enjoy deeper sleep by balancing stress hormones and regulating circadian rhythms.
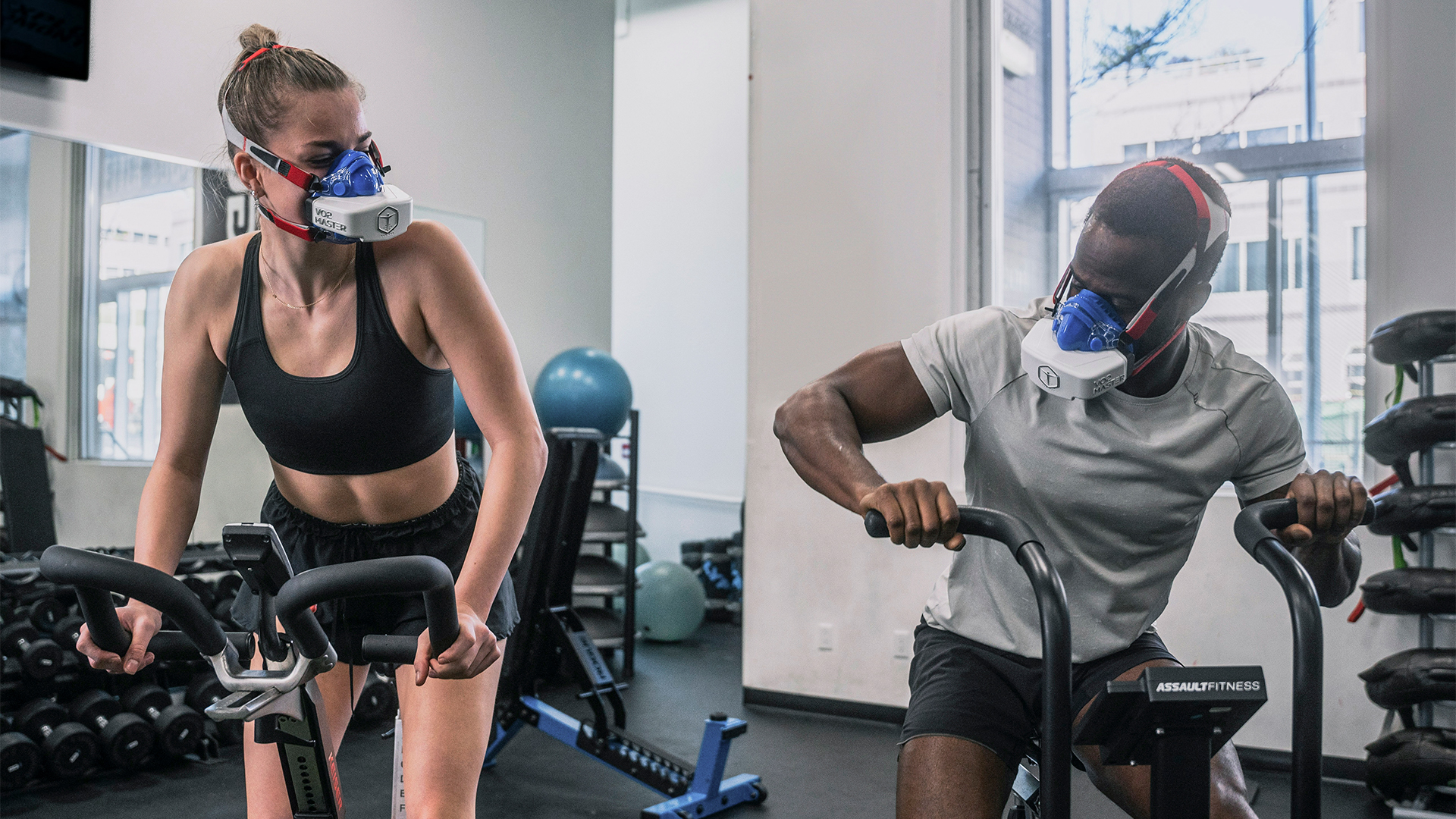

VO2 max, or maximal oxygen uptake, measures the highest amount of oxygen your body can use during intense exercise. It’s an essential indicator of cardiovascular fitness and reflects your aerobic capacity.
The higher your VO2 max, the more efficient your body is at delivering and using oxygen during workouts.
Increased Endurance: A higher VO2 max means your body can sustain longer periods of exercise without fatigue.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Improved oxygen use helps your body perform activities more efficiently, which is crucial for both athletes and everyday fitness enthusiasts.
Lowered Risk of Chronic Disease: A higher VO2 max is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and other metabolic conditions.
Better Recovery: Individuals with a higher VO2 max recover faster after physical activity due to better oxygenation and nutrient delivery to muscles.
Improving your VO2 max involves structured cardiovascular training, such as:
High—Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of high—intensity exercise followed by rest periods help push your body to use oxygen more effectively.
Steady—State Cardio: Activities like running, cycling, and swimming at a moderate pace for an extended period build endurance and improve oxygen uptake over time.
Progressive Overload: Gradually increasing the intensity or duration of your aerobic workouts helps boost your VO2 max.
VO2 max is closely linked to your heart’s ability to pump blood and deliver oxygen to muscles. Regular aerobic exercise increases your body’s capillary network, allowing more oxygen to be transported to working muscles. This results in:
Improved stroke volume of the heart, so it pumps more blood per beat.
Increased lung capacity, aiding in better oxygen intake.
Enhanced mitochondrial function, allowing your muscles to produce energy more efficiently.
Cardiovascular fitness is not just about burning calories or losing weight; it’s about nurturing your body’s most vital functions and enhancing your quality of life.
Integrating a mix of aerobic exercises into your weekly routine can lead to profound health benefits, improving everything from heart and lung function to mental well—being and longevity. So, whether you’re running, cycling, or joining a high—energy class, keep moving to keep thriving!
Get the latest industry insights, fitness tips, and exclusive offers delivered straight to your inbox.
No spam, just inspiration.